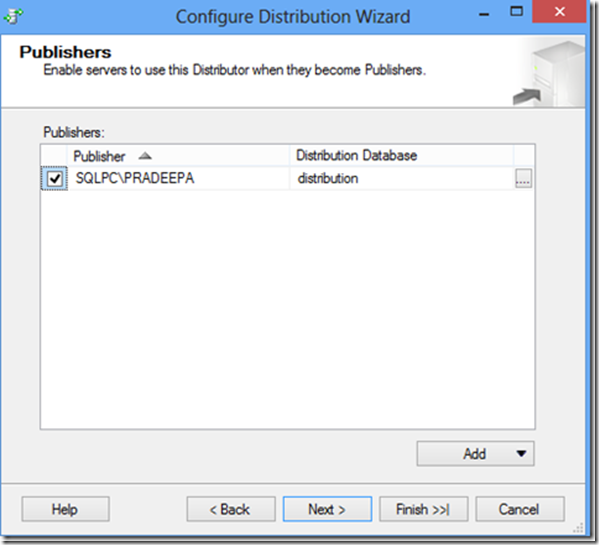
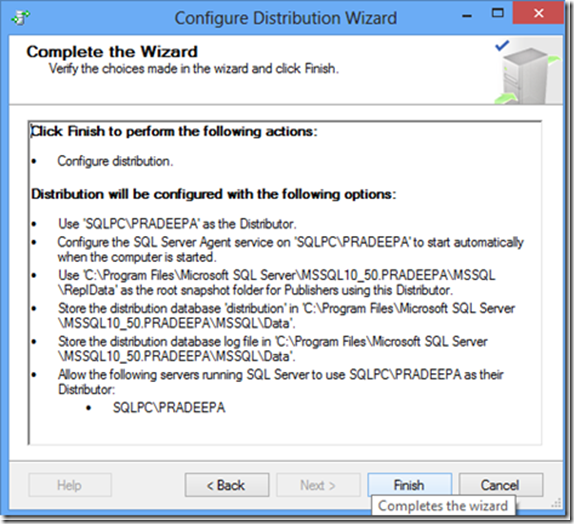
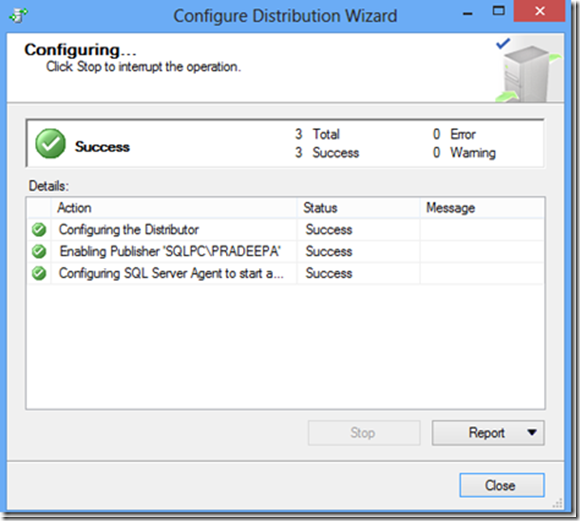
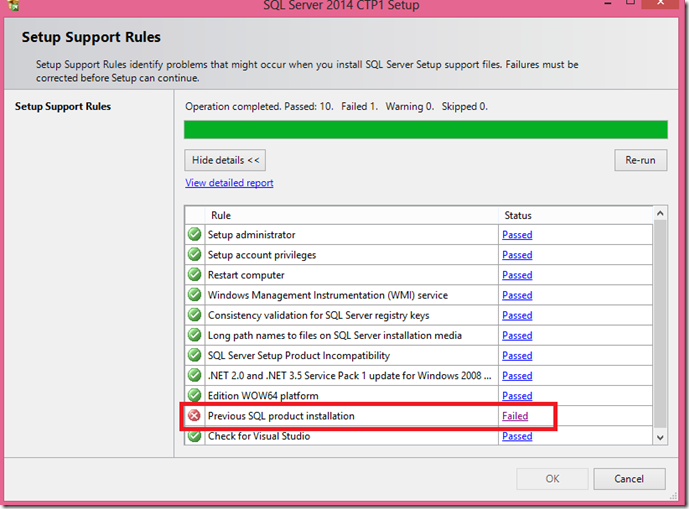
SQL Server setup would fail with below error in message box “Failed to retrieve data for this request”
{
TITLE: SQL Server Setup failure.
——————————
SQL Server Setup has encountered the following error:
Failed to retrieve data for this request..
For help, click: http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink?LinkID=20476&ProdName=Microsoft%20SQL%20Server&EvtSrc=setup.rll&EvtID=50000&EvtType=0xE8A0C283%25400xAC7B1A58%25401233%254053
——————————
BUTTONS:
OK
}
In Summary.txt you will notice error similar to one below
Overall summary:
Final result: Failed: see details below
Exit code (Decimal): -2146233088
Exit facility code: 19
Exit error code: 5376
Exit message: Failed to retrieve data for this request.
Start time: 2015-02-19 19:48:58
End time: 2015-02-19 19:50:47
Requested action: Install
Exception help link: http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink?LinkId=20476&ProdName=Microsoft+SQL+Server&EvtSrc=setup.rll&EvtID=50000&ProdVer=12.0.2342.0&EvtType=0xE8A0C283%400xAC7B1A58%401233%4053&EvtType=0xE8A0C283%400xAC7B1A58%401233%4053
Exception summary:
The following is an exception stack listing the exceptions in outermost to innermost order
Inner exceptions are being indented
Exception type: Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Sdk.Sfc.EnumeratorException
Message:
Failed to retrieve data for this request.
HResult : 0x80131500
Data:
HelpLink.ProdName = Microsoft SQL Server
HelpLink.BaseHelpUrl = http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink
HelpLink.LinkId = 20476
HelpLink.EvtType = 0xE8A0C283@0xAC7B1A58@1233@53
DisableWatson = true
Stack:
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Sdk.Sfc.Enumerator.Process(Object connectionInfo, Request request)
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Chainer.Infrastructure.SqlDiscoveryDatastoreInterface.ProcessDTbl(DataTable dt, Int32 level)
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Chainer.Infrastructure.SqlDiscoveryDatastoreInterface.CollectSqlDiscoveryData(String machineName)
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Chainer.Infrastructure.SqlDiscoveryDatastoreInterface.CollectDiscoveryData(String machineName)
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Chainer.Infrastructure.SqlDiscoveryDatastoreInterface.LoadData(IEnumerable`1 machineNames, String discoveryDocRootPath, String clusterDiscoveryDocRootPath)
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Configuration.SetupExtension.RunDiscoveryAction.ExecuteAction(String actionId)
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Chainer.Infrastructure.Action.Execute(String actionId, TextWriter errorStream)
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Setup.Chainer.Workflow.ActionInvocation.<>c__DisplayClasse.<ExecuteActionWithRetryHelper>b__b()
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Setup.Chainer.Workflow.ActionInvocation.ExecuteActionHelper(ActionWorker workerDelegate)
Inner exception type: Microsoft.SqlServer.Configuration.Sco.SqlRegistryException
Message:
The network path was not found.
HResult : 0x84d10035
FacilityCode : 1233 (4d1)
ErrorCode : 53 (0035)
Data:
WatsonData = Microsoft.SqlServer.Configuration.Sco.SqlRegistryException@Win32Error
Stack:
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Configuration.Sco.SqlRegistry.CreateBaseKey(ServiceContainer ctx, String machineName, IntPtr hKey, String keyName, RegistryAccess access, RegistryView view)
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Configuration.Sco.SqlRegistry.GetLocalMachine(ServiceContainer ctx, String machineName, RegistryAccess access, RegistryView view)
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Discovery.DiscoveryUtils.GetLocalMachineRootKey(ServiceContainer ctx, String machineName, RegistryView registryView)
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Discovery.DiscoveryUtils.GetLocalMachineSubKey(ServiceContainer ctx, String machineName, RegistryView regView, String regPath, RegistryAccess registryAccess)
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Discovery.DiscoveryEnumObject.GetSql2kMsiInstanceListInHive(String machineName, RegistryView regView)
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Discovery.DiscoveryEnumObject.LoadSql2kInstanceList(String machineName)
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Discovery.Product.GetData(EnumResult erParent)
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Sdk.Sfc.Environment.GetData()
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Sdk.Sfc.Environment.GetData(Request req, Object ci)
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Sdk.Sfc.Enumerator.GetData(Object connectionInfo, Request request)
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Sdk.Sfc.Enumerator.Process(Object connectionInfo, Request request)
Watson error
Watson bucket data:
Bucket param 1: SQL Server 2014@RTM@
Bucket param 2: 0x6785B09D
Bucket param 3: 0xE8A0C283
Bucket param 4: 0x74E34741
Bucket param 5: 0xAC7B1A58@1233@53
Bucket param 6: RunRemoteDiscoveryAction
Bucket param 7:
Bucket param 8:
Bucket param 9: 0xD195CE25
Bucket param 10:
From detail.txt
(01) 2015-02-19 19:49:25 Slp: Discovery on nodename failed due to exception
(01) 2015-02-19 19:49:25 Slp: Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Sdk.Sfc.EnumeratorException: Failed to retrieve data for this request. —> Microsoft.SqlServer.Configuration.Sco.SqlRegistryException: The network path was not found.
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Configuration.Sco.SqlRegistry.CreateBaseKey(ServiceContainer ctx, String machineName, IntPtr hKey, String keyName, RegistryAccess access, RegistryView view)
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Configuration.Sco.SqlRegistry.GetLocalMachine(ServiceContainer ctx, String machineName, RegistryAccess access, RegistryView view)
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Discovery.DiscoveryUtils.GetLocalMachineRootKey(ServiceContainer ctx, String machineName, RegistryView registryView)
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Discovery.DiscoveryUtils.GetLocalMachineSubKey(ServiceContainer ctx, String machineName, RegistryView regView, String regPath, RegistryAccess registryAccess)
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Discovery.DiscoveryEnumObject.GetSql2kMsiInstanceListInHive(String machineName, RegistryView regView)
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Discovery.DiscoveryEnumObject.LoadSql2kInstanceList(String machineName)
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Discovery.Product.GetData(EnumResult erParent)
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Sdk.Sfc.Environment.GetData()
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Sdk.Sfc.Environment.GetData(Request req, Object ci)
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Sdk.Sfc.Enumerator.GetData(Object connectionInfo, Request request)
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Sdk.Sfc.Enumerator.Process(Object connectionInfo, Request request)
— End of inner exception stack trace —
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Sdk.Sfc.Enumerator.Process(Object connectionInfo, Request request)
Resolution
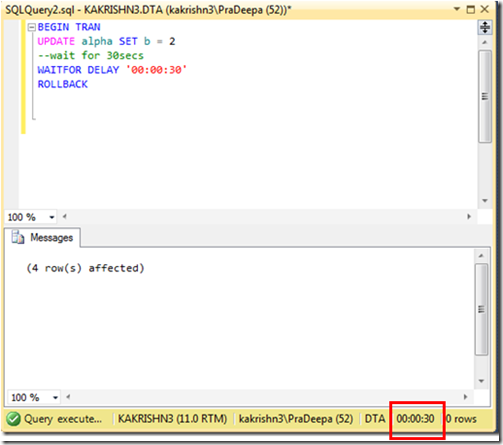
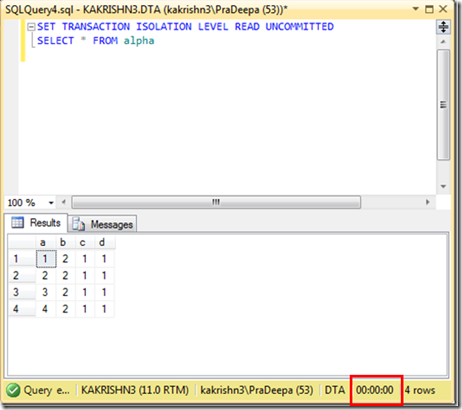
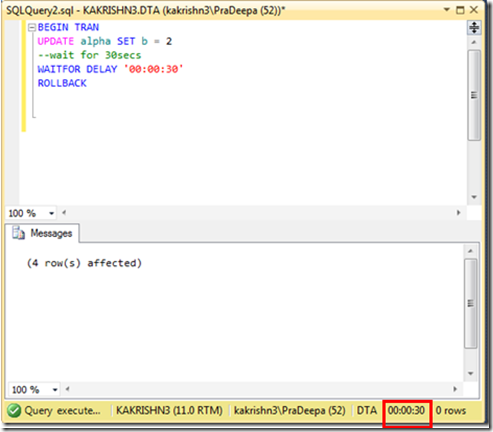
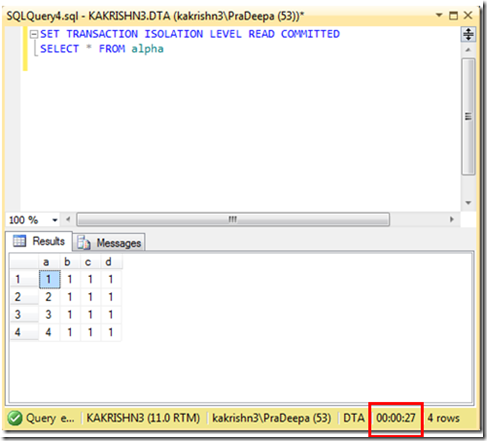
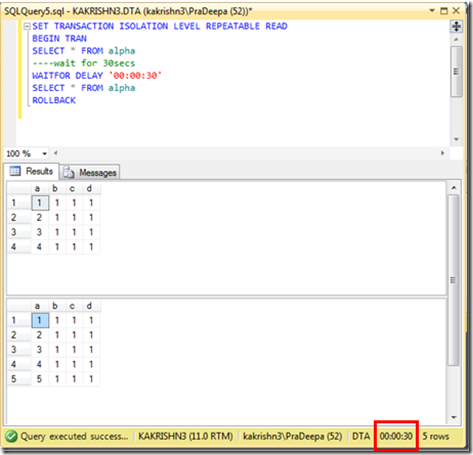
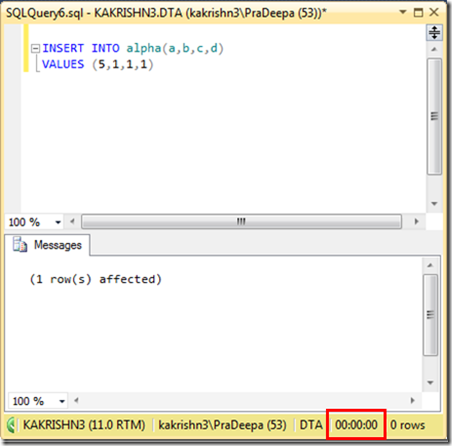
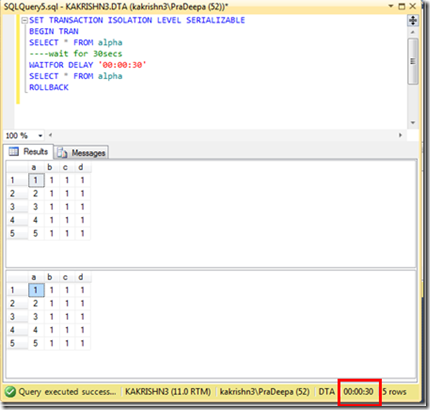
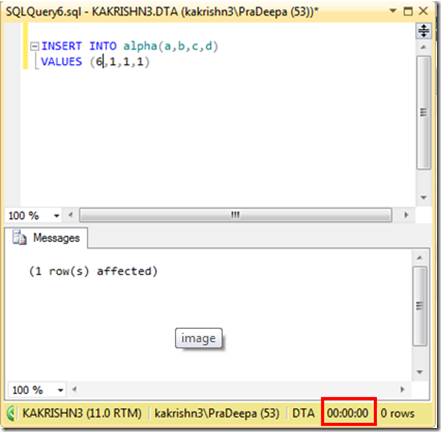
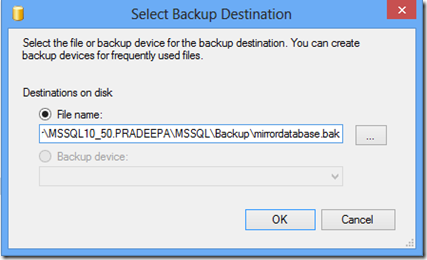
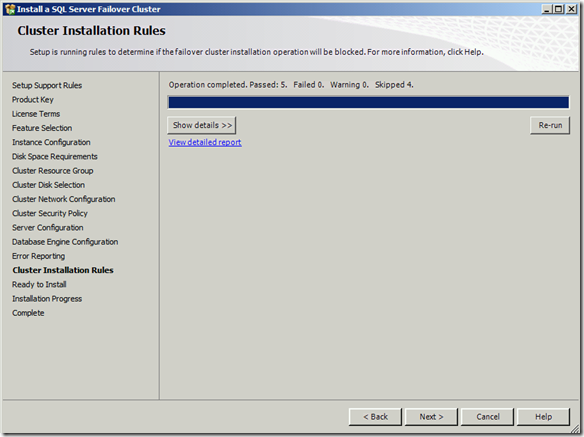
1. Check the connectivity between node from which you are installing SQL Server to other nodes. (\\Othernodes should work when you are installing SQL on box which is part of windows cluster regardless of SQL Cluster).
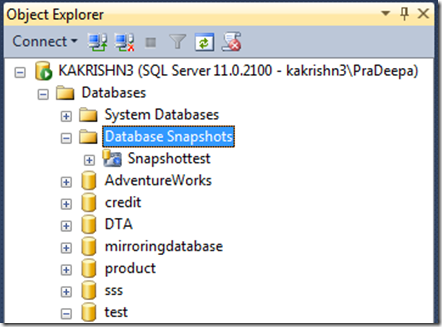
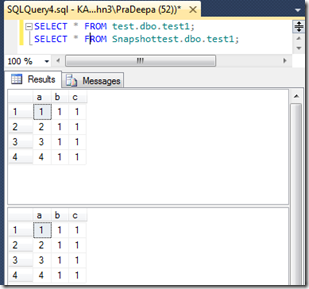
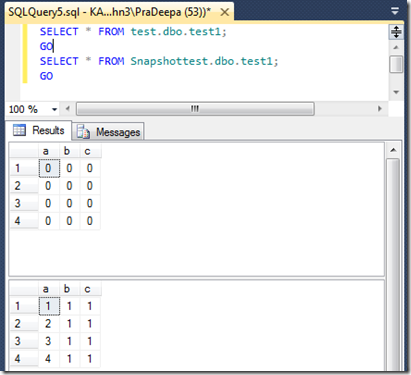
![clip_image001[8] clip_image001[8]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image0018_thumb4.png?w=631&h=524)
![clip_image001[4] clip_image001[4]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image0014_thumb6.png?w=497&h=552)
![clip_image001[4] clip_image001[4]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image0014_thumb5.png?w=434&h=441)
![clip_image001[22] clip_image001[22]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00122_thumb2.png?w=474&h=486)
![clip_image001[26] clip_image001[26]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00126_thumb2.png?w=484&h=492)
![clip_image001[24] clip_image001[24]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00124_thumb2.png?w=477&h=487)
![clip_image001[28] clip_image001[28]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00128_thumb2.png?w=486&h=496)
![clip_image001[30] clip_image001[30]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00130_thumb2.png?w=500&h=508)
![clip_image001[32] clip_image001[32]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00132_thumb2.png?w=518&h=531)
![clip_image001[34] clip_image001[34]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00134_thumb2.png?w=528&h=539)
![clip_image001[36] clip_image001[36]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00136_thumb1.png?w=516&h=527)
![clip_image001[4] clip_image001[4]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image0014_thumb4.png?w=524&h=489)
![clip_image001[6] clip_image001[6]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image0016_thumb4.png?w=522&h=485)
![clip_image001[8] clip_image001[8]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image0018_thumb3.png?w=529&h=490)
![clip_image001[10] clip_image001[10]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00110_thumb1.png?w=514&h=457)
![clip_image001[12] clip_image001[12]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00112_thumb1.png?w=525&h=488)
![clip_image001[14] clip_image001[14]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00114_thumb1.png?w=527&h=490)
![clip_image001[16] clip_image001[16]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00116_thumb3.png?w=533&h=443)
![clip_image001[3] clip_image001[3]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image0013_thumb.png?w=825&h=226)
![clip_image001[5] clip_image001[5]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image0015_thumb.png?w=512&h=593)
![clip_image001[4] clip_image001[4]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image0014_thumb2.png?w=484&h=414)
![clip_image001[6] clip_image001[6]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image0016_thumb2.png?w=489&h=455)
![clip_image001[8] clip_image001[8]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image0018_thumb2.png?w=448&h=415)
![clip_image001[16] clip_image001[16]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00116_thumb2.png?w=456&h=424)
![clip_image001[18] clip_image001[18]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00118_thumb1.png?w=457&h=426)
![clip_image001[20] clip_image001[20]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00120_thumb1.png?w=451&h=343)
![clip_image001[22] clip_image001[22]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00122_thumb1.png?w=442&h=411)
![clip_image001[24] clip_image001[24]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00124_thumb1.png?w=460&h=426)
![clip_image001[26] clip_image001[26]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00126_thumb1.png?w=456&h=424)
![clip_image001[28] clip_image001[28]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00128_thumb1.png?w=453&h=423)
![clip_image001[30] clip_image001[30]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00130_thumb1.png?w=440&h=409)
![clip_image001[32] clip_image001[32]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00132_thumb1.png?w=439&h=408)
![clip_image001[34] clip_image001[34]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00134_thumb1.png?w=446&h=413)
![clip_image001[38] clip_image001[38]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00138_thumb1.png?w=420&h=494)
![clip_image001[6] clip_image001[6]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image0016_thumb3.png?w=455&h=563)
![clip_image001[4] clip_image001[4]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image0014_thumb3.png?w=459&h=570)
![clip_image001[4] clip_image001[4]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image0014_thumb.png?w=513&h=459)
![clip_image001[6] clip_image001[6]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image0016_thumb.png?w=432&h=99)
![clip_image001[8] clip_image001[8]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image0018_thumb.png?w=423&h=447)
![clip_image002[4] clip_image002[4]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image0024_thumb.png?w=530&h=477)
![clip_image001[16] clip_image001[16]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00116_thumb.png?w=382&h=532)
![clip_image001[18] clip_image001[18]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00118_thumb.png?w=550&h=406)
![clip_image001[20] clip_image001[20]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00120_thumb.png?w=551&h=497)
![clip_image001[22] clip_image001[22]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00122_thumb.png?w=548&h=489)
![clip_image001[24] clip_image001[24]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00124_thumb.png?w=558&h=122)
![clip_image001[26] clip_image001[26]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00126_thumb.png?w=342&h=574)
![clip_image001[28] clip_image001[28]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00128_thumb.png?w=550&h=494)
![clip_image001[30] clip_image001[30]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00130_thumb.png?w=550&h=500)
![clip_image001[32] clip_image001[32]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00132_thumb.png?w=550&h=497)
![clip_image001[34] clip_image001[34]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00134_thumb.png?w=551&h=501)
![clip_image001[36] clip_image001[36]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00136_thumb.png?w=455&h=340)
![clip_image001[38] clip_image001[38]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00138_thumb.png?w=528&h=478)
![clip_image001[40] clip_image001[40]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00140_thumb.png?w=529&h=476)
![clip_image001[42] clip_image001[42]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00142_thumb.png?w=453&h=410)
![clip_image001[44] clip_image001[44]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00144_thumb.png?w=444&h=402)
![clip_image001[46] clip_image001[46]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00146_thumb.png?w=561&h=243)
![clip_image001[48] clip_image001[48]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00148_thumb.png?w=562&h=504)
![clip_image001[50] clip_image001[50]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00150_thumb.png?w=322&h=517)
![clip_image001[52] clip_image001[52]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00152_thumb.png?w=662&h=451)
![clip_image001[4] clip_image001[4]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image0014_thumb1.png?w=563&h=575)
![clip_image001[6] clip_image001[6]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image0016_thumb1.png?w=576&h=502)
![clip_image001[8] clip_image001[8]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image0018_thumb1.png?w=583&h=508)
![clip_image001[10] clip_image001[10]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00110_thumb.png?w=587&h=511)
![clip_image001[12] clip_image001[12]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00112_thumb.png?w=599&h=522)
![clip_image001[14] clip_image001[14]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00114_thumb.png?w=606&h=548)
![clip_image001[16] clip_image001[16]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/clip_image00116_thumb1.png?w=562&h=295)
![clip_image001[4] clip_image001[4]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image0014_thumb4.png?w=513&h=380)
![clip_image001[6] clip_image001[6]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image0016_thumb4.png?w=548&h=407)
![clip_image001[28] clip_image001[28]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00128_thumb4.png?w=601&h=452)
![clip_image001[12] clip_image001[12]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00112_thumb3.png?w=527&h=392)
![clip_image001[14] clip_image001[14]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00114_thumb3.png?w=528&h=392)
![clip_image001[16] clip_image001[16]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00116_thumb4.png?w=524&h=396)
![clip_image001[18] clip_image001[18]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00118_thumb4.png?w=543&h=407)
![clip_image001[20] clip_image001[20]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00120_thumb4.png?w=644&h=473)
![clip_image001[24] clip_image001[24]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00124_thumb4.png?w=642&h=480)
![clip_image001[26] clip_image001[26]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00126_thumb3.png?w=642&h=482)
![clip_image001[1] clip_image001[1]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image0011_thumb1.png?w=597&h=446)
![clip_image001[30] clip_image001[30]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00130_thumb4.png?w=589&h=414)
![clip_image001[4] clip_image001[4]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image0014_thumb3.png?w=352&h=324)
![clip_image001[6] clip_image001[6]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image0016_thumb3.png?w=457&h=413)
![clip_image001[8] clip_image001[8]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image0018_thumb3.png?w=452&h=405)
![clip_image001[10] clip_image001[10]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00110_thumb2.png?w=459&h=412)
![clip_image001[12] clip_image001[12]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00112_thumb2.png?w=463&h=419)
![clip_image001[14] clip_image001[14]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00114_thumb2.png?w=468&h=424)
![clip_image001[16] clip_image001[16]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00116_thumb3.png?w=521&h=366)
![clip_image001[18] clip_image001[18]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00118_thumb3.png?w=522&h=470)
![clip_image001[20] clip_image001[20]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00120_thumb3.png?w=533&h=489)
![clip_image001[22] clip_image001[22]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00122_thumb3.png?w=490&h=415)
![clip_image001[24] clip_image001[24]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00124_thumb3.png?w=503&h=457)
![clip_image001[26] clip_image001[26]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00126_thumb2.png?w=508&h=462)
![clip_image001[28] clip_image001[28]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00128_thumb3.png?w=508&h=462)
![clip_image001[30] clip_image001[30]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00130_thumb3.png?w=489&h=432)
![clip_image001[32] clip_image001[32]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00132_thumb3.png?w=521&h=372)
![clip_image001[34] clip_image001[34]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00134_thumb3.png?w=517&h=489)
![clip_image001[36] clip_image001[36]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00136_thumb4.png?w=506&h=456)
![clip_image001[38] clip_image001[38]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00138_thumb4.png?w=504&h=452)
![clip_image001[40] clip_image001[40]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00140_thumb4.png?w=510&h=459)
![clip_image001[42] clip_image001[42]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00142_thumb3.png?w=523&h=469)
![clip_image001[46] clip_image001[46]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00146_thumb3.png?w=539&h=452)
![clip_image001[44] clip_image001[44]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00144_thumb3.png?w=414&h=504)
![clip_image001[48] clip_image001[48]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00148_thumb2.png?w=483&h=435)
![clip_image001[50] clip_image001[50]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00150_thumb2.png?w=486&h=444)
![clip_image001[52] clip_image001[52]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00152_thumb2.png?w=480&h=432)
![clip_image001[54] clip_image001[54]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00154_thumb2.png?w=479&h=437)
![clip_image001[56] clip_image001[56]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00156_thumb2.png?w=480&h=428)
![clip_image001[58] clip_image001[58]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00158_thumb2.png?w=428&h=318)
![clip_image001[20] clip_image001[20]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00120_thumb2.png?w=487&h=175)
![clip_image001[22] clip_image001[22]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00122_thumb2.png?w=343&h=376)
![clip_image001[4] clip_image001[4]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image0014_thumb2.png?w=552&h=331)

![clip_image001[6] clip_image001[6]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image0016_thumb1.png?w=495&h=301)
![clip_image001[10] clip_image001[10]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00110_thumb.png?w=539&h=483)
![clip_image001[8] clip_image001[8]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image0018_thumb2.png?w=545&h=486)
![clip_image001[12] clip_image001[12]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00112_thumb1.png?w=738&h=371)
![clip_image001[14] clip_image001[14]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00114_thumb.png?w=740&h=379)
![clip_image001[40] clip_image001[40]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00140_thumb3.png?w=678&h=341)
![clip_image001[42] clip_image001[42]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00142_thumb2.png?w=693&h=354)
![clip_image001[16] clip_image001[16]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00116_thumb2.png?w=490&h=289)
![clip_image001[18] clip_image001[18]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00118_thumb2.png?w=485&h=435)
![clip_image001[24] clip_image001[24]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00124_thumb2.png?w=553&h=489)
![clip_image001[28] clip_image001[28]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00128_thumb2.png?w=610&h=312)
![clip_image001[30] clip_image001[30]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00130_thumb2.png?w=609&h=302)
![clip_image001[32] clip_image001[32]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00132_thumb2.png?w=507&h=320)
![clip_image001[34] clip_image001[34]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00134_thumb2.png?w=508&h=458)
![clip_image001[36] clip_image001[36]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00136_thumb3.png?w=677&h=343)
![clip_image001[38] clip_image001[38]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00138_thumb3.png?w=682&h=340)
![clip_image001[16] clip_image001[16]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00116_thumb1.png?w=483&h=453)
![clip_image001[18] clip_image001[18]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00118_thumb1.png?w=490&h=445)
![clip_image001[20] clip_image001[20]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00120_thumb1.png?w=498&h=447)
![clip_image001[22] clip_image001[22]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00122_thumb1.png?w=527&h=475)
![clip_image001[24] clip_image001[24]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00124_thumb1.png?w=516&h=467)
![clip_image001[26] clip_image001[26]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00126_thumb1.png?w=523&h=475)
![clip_image001[28] clip_image001[28]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00128_thumb1.png?w=533&h=482)
![clip_image001[30] clip_image001[30]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00130_thumb1.png?w=539&h=492)
![clip_image001[32] clip_image001[32]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00132_thumb1.png?w=466&h=408)
![clip_image001[34] clip_image001[34]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00134_thumb1.png?w=502&h=454)
![clip_image001[36] clip_image001[36]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00136_thumb2.png?w=526&h=441)
![clip_image001[38] clip_image001[38]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00138_thumb2.png?w=536&h=487)
![clip_image001[40] clip_image001[40]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00140_thumb2.png?w=547&h=490)
![clip_image001[42] clip_image001[42]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00142_thumb1.png?w=428&h=225)
![clip_image001[44] clip_image001[44]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00144_thumb2.png?w=428&h=377)
![clip_image001[46] clip_image001[46]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00146_thumb2.png?w=487&h=439)
![clip_image001[48] clip_image001[48]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00148_thumb1.png?w=497&h=452)
![clip_image001[50] clip_image001[50]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00150_thumb1.png?w=504&h=456)
![clip_image001[52] clip_image001[52]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00152_thumb1.png?w=503&h=432)
![clip_image001[54] clip_image001[54]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00154_thumb1.png?w=405&h=497)
![clip_image001[56] clip_image001[56]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00156_thumb1.png?w=416&h=370)
![clip_image001[58] clip_image001[58]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00158_thumb1.png?w=456&h=411)
![clip_image001[60] clip_image001[60]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00160_thumb1.png?w=454&h=411)
![clip_image001[62] clip_image001[62]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00162_thumb1.png?w=455&h=414)
![clip_image001[64] clip_image001[64]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00164_thumb1.png?w=478&h=433)
![clip_image001[66] clip_image001[66]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00166_thumb1.png?w=477&h=298)
![clip_image001[68] clip_image001[68]](https://sqlserverscribbles.files.wordpress.com/2013/06/clip_image00168_thumb1.png?w=496&h=465)